Introduction: Incineration of spent wash is one of the tested & proven technologies for the disposal of spent wash for zero liquid discharge (ZLD).
Sitson was experimenting since 1994, the first experiment at M/S. Pravara Paper Mill mixing with bagasse and burning in a fluidized bed boiler. The second experiment was in 1995 at M/S. Krishna S.S.K., DIEG project of VSI Pune, where the boiler and power portion were designed, erected and commissioned by Sitson. Power technology was used for spent wash conversion.
The Boiler was generating hot air in addition to steam. This hot air was used for spraying in the spray drier. The boiler was a fluidized bed boiler with a facility to burn coal and bagasse spent wash powder. The third experiment of burning biogas spent washed along with the LDO fire tube boiler which was working satisfactorily. Sitson has supplied more than 40 boilers where biogas is burnt in bagasse-fired boilers.
Now Sitson has designed and supplied spent wash incineration boilers for concentrated spent wash with support fuels like biogas, coal and biomass. Sitson has both technologies,
- Fluidized bed boilers and
- Travelling grate boilers
The main requirement in incineration boilers is
- Burning of concentrated spent wash in required quantity along with supporting fuel
- Trouble-free boiler operation without maintenance and longer periods of operation without any cleaning required in between
- To maintain pollution control board norms
- There should not be any unburnt slop in ash which ensures no contamination of water/effluent
- Travelling grate boilers
This is the best option for supporting fuel bagasse, rice husk, coal and biomass. Sitson could achieve all these requirements at,
- L.H. Sugar Factories Ltd., Pilibhit, U.P.
- Sir Shadilal Enterprises Ltd. U.P.
- Yedeshwari Agro Products Ltd., Pune, M.S.
- Cooperative Company Ltd., Saharanpur, U.P.
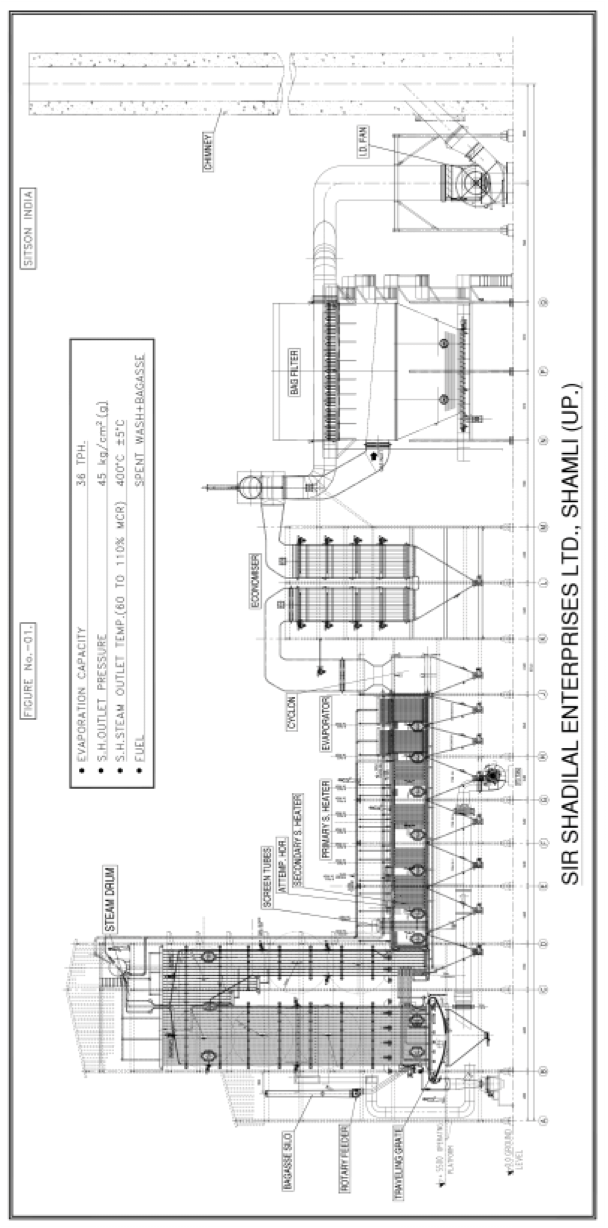
Boiler specifications at L.H. Sugar and Sir Shadilal Enterprises
Boiler capacity – 36TPH
Pressure – 45 Kg/cm2 (g)
Steam temp. – 415 deg. C
Supporting fuel – bagasse
Quantity of conc. spent wash (60deg. Brix) burn- up to 16 t/h
Observations
- The boiler is running without any stoppage for cleaning between even up to 250 days of working
- The ash is dry creamish in colour and not sticky
- The boiler was run only on concentrated spent wash for @6 hrs. without any support fuel. No problem was observed
- As the ash is dry Sitson started offering ESP instead of bag filters
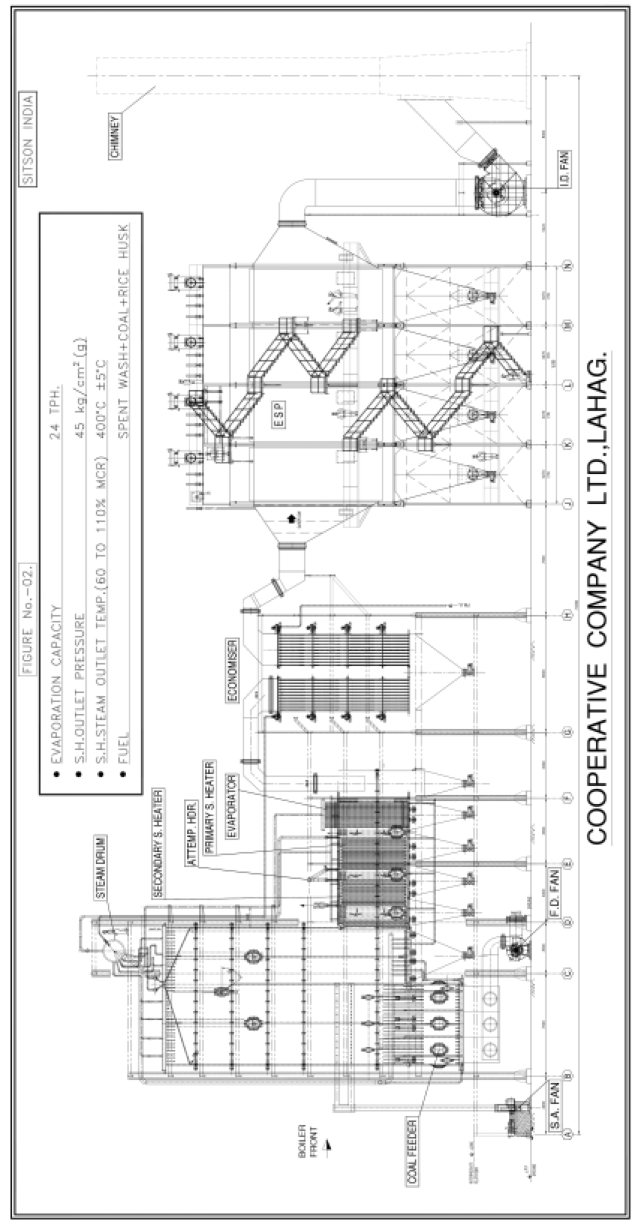
B. Fluidized Bed Boilers
This is the best option for supporting fuel coal and/or rice husk. The fluidized bed boiler- 24 TPH/42 KGC pressure/415℃ temp., at M/s. Lahag Group in UP can burn coal and rise husk as a support fuel. Since the ash content is more in coal and rice husk it is self-cleaning and hence boiler can run without any cleaning during operation even for a year. For coal and rice husk as support fuel, this is the best technology.
Sitson can make provision to burn bagasse up to 50% in AFBC boilers as we have tried in biomass-fired AFBC boilers at various places.
The points to be looked into are
- Proper placement of H.S. of a boiler, S.H., evaporators and economizers
- Proper soot-blowing arrangements
- Proper ash removal arrangements
- Proper design of travelling grate
- Proper design of ESP or bag filters
- Proper design of conc. spent wash feeding and burner system
Spent wash generation with respect to feedstock for 60KLPD ethanol plant:
| Sr no. | Feedstock | Feedstock Requirement | Ethanol Yield | Spent wash incineration |
| 1 | Cane juice | 800 t/d sugar cane | 75 litre/MT | 385 tpd (solid 4%) 24 tpd (solid 58%) |
| 2 | B-Heavy Molasses | 190 MT/Day | 315 litre/MT | 510 tpd (solid 12%) 102 tpd (Solid 58%) |
| 3 | C-Molasses | 240 MT/Day | 250 litre/MT | 624 tpd (solid 15%) 168 tpd (solid 58%) |
Other Technologies besides Incineration.
- Spent wash evaporator for an incinerator
- Spent wash evaporator followed by ATFD
- Biodigestor followed by MEE
- Biodigestor followed by MEE + ATFD
Conclusion
Advantages of Incineration boiler from spent wash:
- Saving in fuel costs by burning concentrated spent wash in the boiler reduced fuel required for a boiler
- Recycling more water into the system as we have concentrated
- Meet the norms of ZDL as bio-composting is not allowed nowadays
- Though the initial cost is more, which can be recovered within 2-3 years for other methods additional fuel required is more
Note:
- A typical general arrangement drawing for a travelling grate boiler suitable for spent wash + bagasse or coal or rice husk is as per Fig. – I attached
- A typical general arrangement drawing for AFBC boiler suitable for spent wash + coal or rice husk is as per Fig. – II attached
Trends in distillery spent wash incineration technology
Typical case of distilleries today
- One of the most important environmental problems faced by the world is the management of waste
- Pollution prevention focuses on preventing the generation of waste, while waste minimization refers to reducing the volume or toxicity of hazardous wastes by water recycling and reuse and process modifications and the by-product recovery as a fall out of the manufacturing process creates ample scope for revenue generation thereby offsetting the costs substantially
- The aqueous distillery effluent stream known as the spent wash is a dark brown highly organic effluent and is approximately 12-15 times by volume of the product alcohol. It is one of the most complex, troublesome and strongest organic industrial effluents, having extremely high COD and BOD values. Because of the high concentration of organic load, distillery-spent wash can be a potential source of renewable energy if handled properly
Introduction to distillery waste:
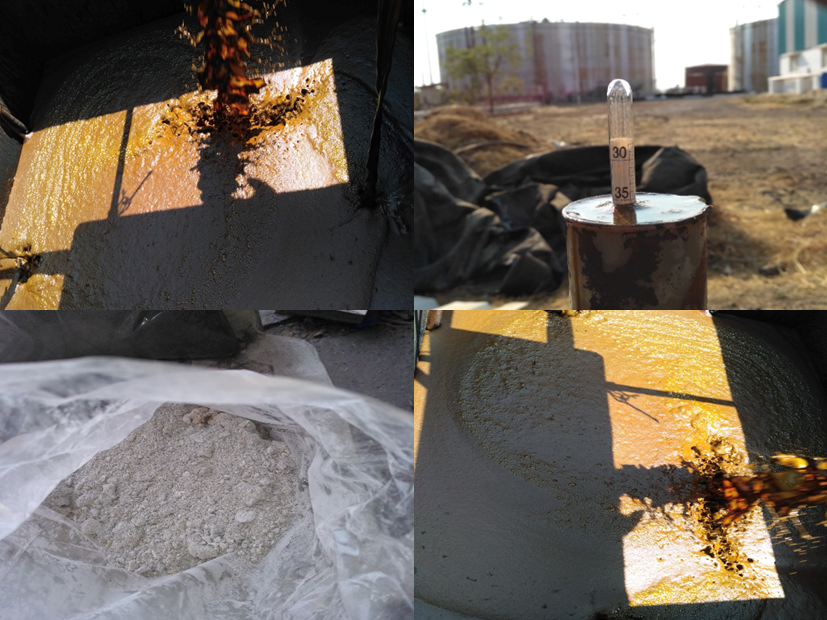

Challenges in slop combustion
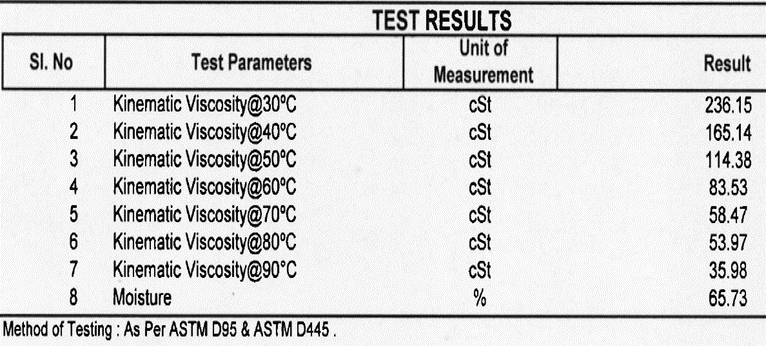
- Low calorific value of slop even at 60Brix (1200Kcals/Kg). However, it fluctuates between 45 to 60Brix
- Low ash fusion temperature due to high alkali constituents in ash(K2O+Na2O)
- High chlorides (>1%), calcium oxide and sulfate ash
- Low silica in ash
- Ensuring continuous operation
Typical case of distilleries today
- EARSTWHILE EFFLUENT TREATMENT SOLUTION: Bio-methanation followed by composting using press mud from a sugar plant
- ‘FORCED / INFLUENCED’ NEW SOLUTION: Incineration of spent wash. Due to the ‘limitation’ in design available, RAW SW was incinerated with support fuel (coal/bagasse). Solution claimed to be a technological innovation but not in the REAL sense
- ENERGY IMBALANCE DUE TO NEW SOLUTION: High steam and power generation than required so distilleries moved away from energy efficiency due to excess energy (steam) available
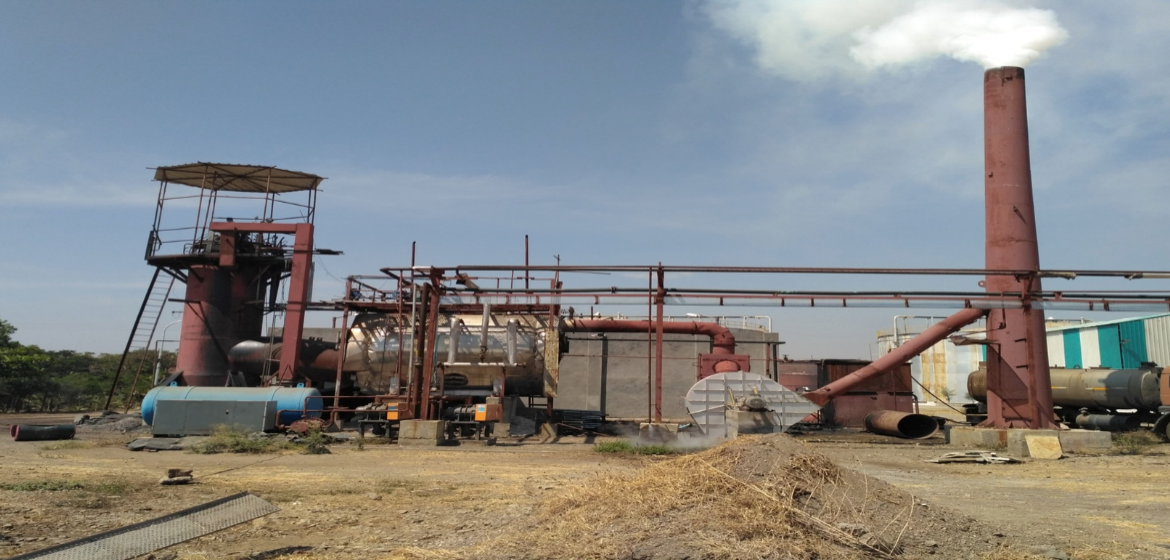
- HIGHER COST OF O&M: Operation cost increased; cement kiln maintenance cost increased 15tph, 45 Kg/Cm2g, 410oC bio-methane spent wash incineration boiler at Utopian Sugars Ltd., Solapur (*PATENTED)


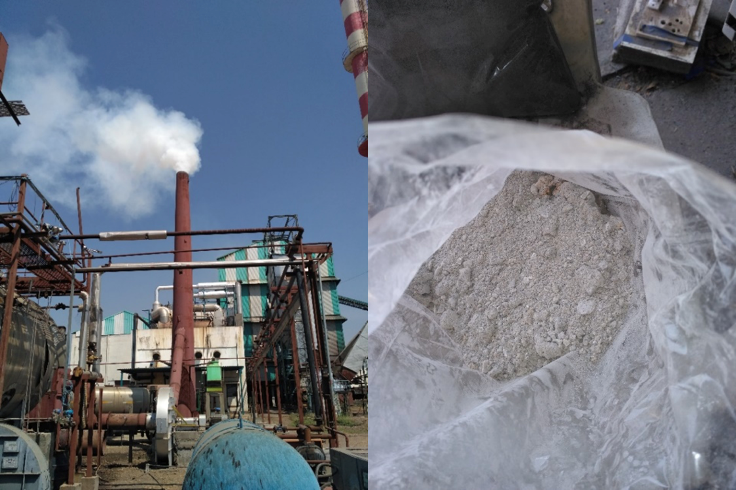
Highlights Of ‘ESBEE’ technology:
- NO FUEL COST (SINCE NO SUPPORT FUEL IS REQUIRED). Hence the cost of operation of the distillery (production cost of ethanol) is lower
- PERFECT ENERGY BALANCE (STEAM AND POWER PRODUCED MATCHES WITH STEAM AND POWER REQUIRED)
- HIGH-QUALITY ASH – Ash generation is only of the spent wash burnt, which is rich in potash
- FULLY AUTOMATIC OPERATION – Operation through BMS system. Skilled operators not required
- HIGH RELIABILITY AND AVAILABILITY – Less ash, less dependency on operators, online cleaning mechanism

Author
Director
Prashant S Bahirgonde
Esbee Power Solutions Pvt. Ltd.