Name: Hrishikesh Vilas Bawane
Organisation: Thermax Ltd.
Designation: Manager- Quality
Education: DME, AWS – CWI, CWIT – Pune
Head SHOP Quality, Receipt & Shipping, DT & NDT Lab, IBR Cell (Product PU- Heating SBU) at Thermax Ltd. More than 25 years of experience in Boiler Quality. Lead Auditor, welding Inspector.

Name: Imran Ibrahim Mujawar
Organisation: Directorate of Steam Boilers, Govt. of Maharashtra
Designation: Deputy Director
Education: Master’s of Technology in Thermal from Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (formerly REC Bhopal). Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from Government college of Engineering, Aurangabad.
Work as Deputy Director in the Regional office of the Joint Director of Steam Boilers, Pune for effective implementation of The Boilers Act 1923, Indian boiler regulations 1950, Maharashtra Boiler Rules 1962, and Maharashtra Economiser Rules 1965.
- Successfully commissioned Unit-7 250 MW Thermal Power plant of MSPGCL, Parli TPS, Tq- Parli, Dist- Beed.
- Successfully implemented “Mukhya Mantri Saur Krishi Vahini Yojana” in the Latur district while working in MSPGCL, Latur solar project division.
- Topper from Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal in M-Tech thermal.
- Invited from Sandipani Technical Campus (Faculty of Engineering) Kolpa, Tq. Dist. Latur as an Industry Expert for “VCRP-2016” to conduct Technical interviews of participants from Latur, Osmanabad, Beed, and Nanded districts in the year 2016.
- Invited from Vilasrao Deshmukh Foundation’s School of the polytechnic, Latur for delivering a seminar on “Thermal Power plant” in the year 2015.
Abstract
As boilers operate under extreme pressure and temperature fluctuations, a small undetected problem during the manufacturing of the boiler and its pressure parts could lead to a catastrophic failure, resulting in an explosion and loss of property or life. Therefore, the boiler and its components must be sufficiently inspected to ensure that the materials, manufacturing, and testing conform to the requirements of the Indian Boiler Regulations 1950. Appendix – J of the said regulations will describe the mandatory stages for inspection during the manufacturing of the boiler and its components and pressure parts.
General
- The Inspecting Authority/Competent Person shall have access to the works of the manufacturer at all reasonable times and shall inspect the manufacture of the boiler at least at the following stages and may reject any part that does not comply with the requirements of the Indian Boiler Regulations, 1950.
- In case of any doubt, the Inspecting Authority/Competent Person may examine at any stage other than the stages stipulated below.
- The manufacturer shall give prior notice to the Inspecting Authority/Competent Person before reaching each stage.
- Before undertaking any of the stage inspections, the Inspecting Authority/ Competent Person shall satisfy himself that the testing equipment/instrument has been properly calibrated.
Stages of Inspection During Manufacture
A) Shell Type Boilers
a) When the materials are ready for identification with the relevant material test certificates at boiler maker’s works.
- In laying out and cutting the plates, the plate identification mark shall be located so as to be clearly visible after the boiler part is completed. If the plate’s identification mark is unavoidably cut out, it shall be transferred by the manufacturer to another part of the component to the satisfaction of the Inspecting Authority/Competent Person.
- The Inspecting Authority/Competent Person shall identify weld test plate material if production weld tests are required.

b) When the Shell plate and end plates have been formed with plate edges prepared for welding and test plates are attached.
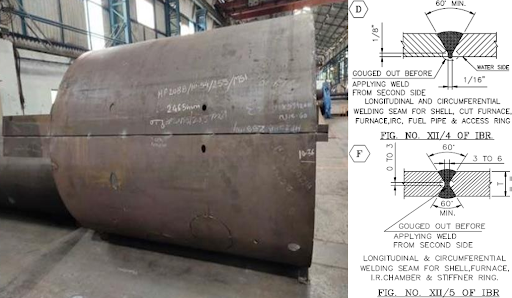
c) When the welding of main cylindrical shell is completed and checked for circularity.

L-Seam – 10% of t & shall not exceed 3mm
C-Seam – 10% of t & shall not exceed 4.8mm
d) To examine radiographs and/or reports of non-destructive testing.
e) When openings have been prepared and stand pipes and similar connections including end plates have been tack-welded in position and subsequently on completion.

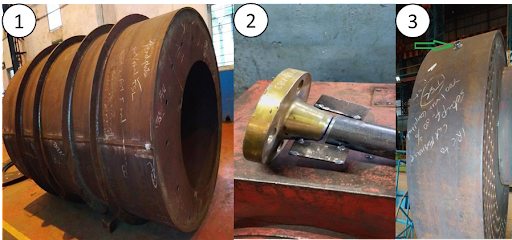
2) Pipe to Flange Setup or Blowdown pipe to flange
3) Coupling Setup
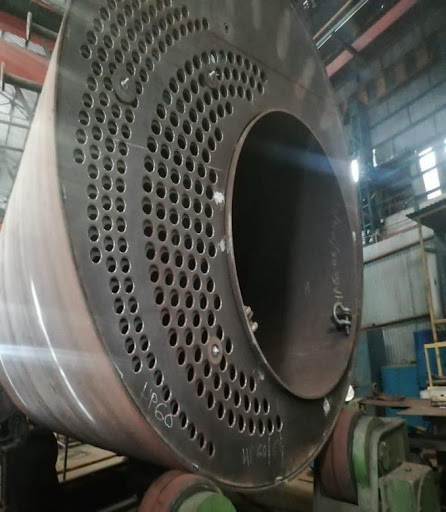




along with Gusset setup
f) When welding of drum or shell is completed and to check the records of heat-treatment when heat treatment is required under these regulations.
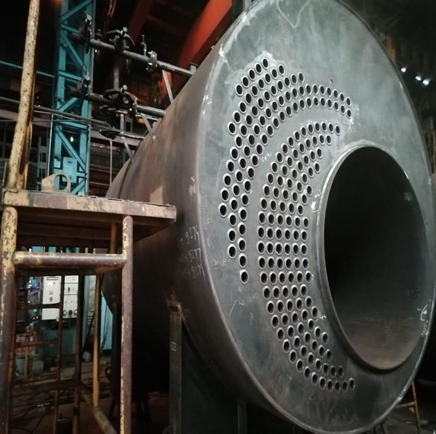


g) When weld test specimens have been prepared from the test plate, previously selected to witness the required testing.
- 02 Nos – Bend Sample (F & R)
- 01 Nos -Transverse Tensile
- 01 Nos -Macro & Micro
- 01 Nos – All Weld Sample
- 03 Nos – V notch Impact sample

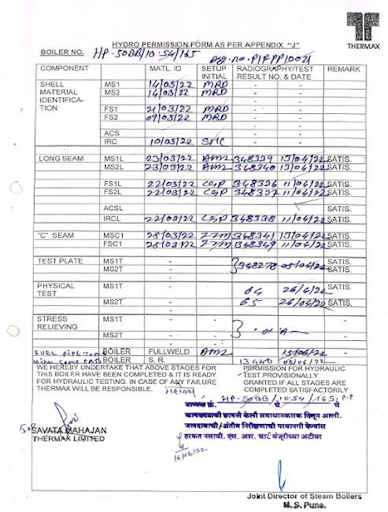
h) During hydraulic test, followed by external and internal examination and stamping.
Hydro pressure=1.5 times design pressure
Required pressure gauge range = 1.5 to 4 times of hydro pressure
| OC Readings and deflections at end plates during hydraulic test | |||
| At 0 Kg/cm2 | At W.P. Kg/cm2 | At hydro press Kg/cm2 | |
| Shell – 1 | |||
| Shell – 2 | |||

B) Water Tube Boilers
Welded drums, headers, separators and vessels:
a) When the materials are ready for identification with the relevant material test certificates at boiler maker’s works;
- In laying out and cutting the plates, the plate identification mark shall be located so as to be clearly visible after the boiler part is completed. If the plate’s identification mark is unavoidably cut out, it shall be transferred by the manufacturer to another part of the component to the satisfaction of the Inspecting Authority / Competent Person.
- The Inspecting Authority/Competent Person shall identify weld test plate material if production weld tests are required
b) When the plates are formed to cylindrical shape with the edges prepared for welding and set up in readiness for commencement of welding and attachment of test plates.
c) When the welding of the main cylindrical shell is completed, the shell checked for circularity and the radiographic or ultrasonic test reports, records are available for scrutiny.
d) When the end plates are ready for identification with the mill certificate, formed to shape with weld edges prepared and set on to the cylindrical shell in readiness for the circumferential welding operation.
e) When the welding of the end plates to the drum or the header is complete and the radiographs or ultrasonic examination records are available for scrutiny.
f) When each drum or header is prepared to receive any compensation plates and attachments, and when at least 10% of each type of branch of tube stub is set up ready for welding.
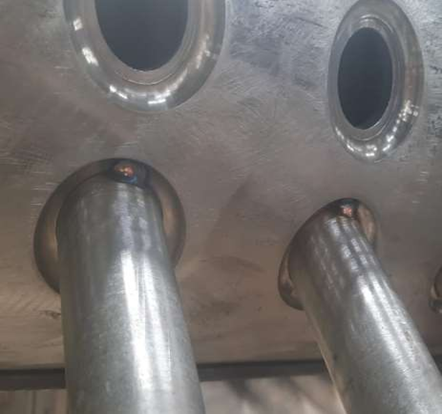


Header to pipe/stub setup
g) When all welding on each drum or header is complete, the Inspecting Authority/Competent Person will check the records of heat treatment, and mark off of specimens for preparation and testing from test plates.
h) During non-destructive examination, after stress relieving, on alloy steel drums and carbon steel drums with carbon content exceeding 0.25 % or thickness more than 100 mm.
i) During hydraulic test followed by final examination and stamping.
Seamless drums, headers, separators and vessels:
a) When materials are ready for identification with the relevant material test certificates, also when each cylinder is prepared for forming, or welding of separate end closures and to identify test plate material
b) When the end plates are ready for identification with the mill certificate, formed to shape with weld edges prepared and set on to the cylindrical shell in readiness for the circumferential welding operation.

c) When the welding of the end plates to the drum or the header is complete and the radiographs or ultrasonic examination records are available for scrutiny.
d) When each drum or header is prepared to receive any compensation plates and attachments, and when at least 10% of each type of branch of tube stub is set up ready for welding.
e) When all welding on each drum or header is complete, the Inspecting Authority will check the records of heat treatment, and mark off of specimens for preparation and testing from test plate.
f) During non-destructive examination, after stress relieving, on alloy steel drums and carbon steel drums with carbon content exceeding 0.25 % or thickness more than 100 mm.
g) During hydraulic test followed by final examination and stamping.
B) Tubular and piping components
a) When the tubes or pipes are ready for identification with the relevant material test certificates at the boiler makers’ works.

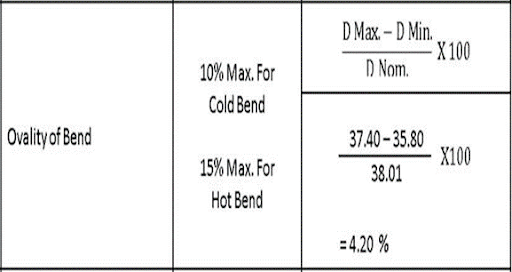
Ovality of bend
Departure from circularity shall not exceed,
10 % – when Bend performed in single bending operation
15 % – When bend which are hot pressed after primary bending


Minimum thickness calculations
If % thinning is more than 25% then PBHT required.
If OD less than 141.3 mm ( 5.5 Inch) & R/OD <= 1.5 PBHT required.
If OD more than 141.3 mm ( 5.5 Inch) & R/OD <= 2.5 PBHT required
R- mean radius of bend to the centre line of tube.
b) When all welding of tubes or pipes and their attachments are complete and the non-destructive examination and stress relieving report/records are available for scrutiny.
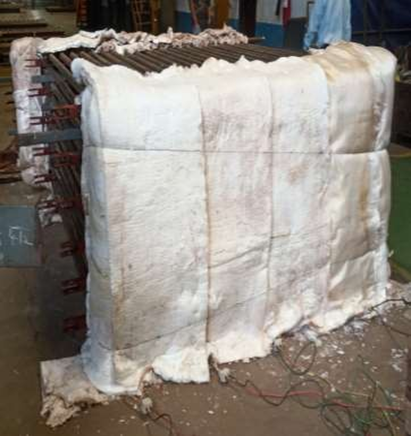
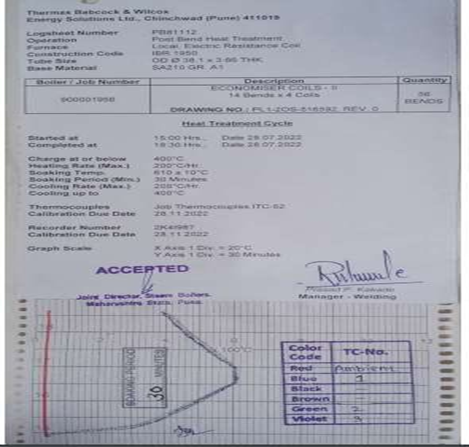

Post Bend heat treatment
c) During hydraulic test followed by final examination and stamping.

C) During hydraulic test followed by final examination and stamping.
a) Steel Makers Works
For manufacture of the billets, ingots, slabs, blooms, plates, bars, concast bars or any other material to be used in the construction of the boilers:
- Checking of the chemistry of steel as per regulations.
- When ready for non-destructive examination and selection of mechanical test specimen after heat treatment.
- Testing, final examination and stamping.
Note: Notwithstanding anything specified above where the steel is made by the Well-known Steel Maker as recognised under the Indian Boiler Regulations, 1950 by the Central Boilers Board these tests will be carried out and certified by the Steel Makers themselves and the records maintained.
b) Pipe and Tube Makers
- Identification of materials with relevant material test certificates.
- When ready for non-destructive examination and selection of mechanical test specimens after heat treatment.
- When specimen is tested and pipes/tubes are ready for hydraulic tests.
- Final inspection and stamping.
Note: Notwithstanding anything specified above, when the pipes/tubes are manufactured by well-known pipes/tubes makers recognised under the Indian Boiler Regulations, 1950 by the Central Boilers Board, all the above stages of inspections shall be carried out and certified by the manufacturers of pipes and tubes themselves and records maintained.
c) Forging Units
- Checking of the chemistry of steel as per regulations.

2. When ready for non-destructive examination and selection of mechanical test specimen after heat treatment.
3. Testing, final examination and stamping.
Note: Notwithstanding anything specified under the Indian Boiler Regulations, 1950 by the Central Boilers Board then tests will above, when the forgings are made by well-known forging units as recognised be carried out and certified by the Forges themselves and all records are maintained properly.
d) Foundry Units
- Checking of the chemistry of molten metal
- Verification of heat number and stamping of test bars

3. Verification of non-destructive examination report and heat treatment reports/records, mechanical testing, final examination & stamping.
Note: Notwithstanding anything specified above, when the castings are made by well-known foundry units as recognised under the Indian Boiler Regulations, 1950 by the Central Boilers Board then tests will be carried out and certified by the Foundries themselves and all records are maintained properly.
e) Valves and Mountings
- Identification of materials with the relevant material test certificates. During this stage raw material along with relevant material test certificates, approved drawings will be checked, raw material should be free from any defects, dimensions should be as per drawings, also valve body shall be clearly marked to indicate the direction of flow etc.


Raw material identification
2. Hydraulic test and stamping
During this stage number of valves and fittings shall be made available to the competent person (excluding mechanical test) shall be as per Reg.290 (e)., Hydraulic testing shall be as per Reg. 290 (a).


Hydro test and final inspection