Bioenergy refers to the energy that is derived from organic matter, such as plant material, animal waste, and wood. Bioenergy can be used for heating, electricity generation, transportation, and other applications.
There are various types of bioenergy, including:
- Biofuels: These are fuels that are made from renewable biological sources, such as ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. Biofuels can be used in transportation and other applications.
- Biomass power: This involves the use of organic matter, such as wood chips, agricultural waste, and municipal solid waste, to generate electricity. Biomass power plants use a variety of technologies, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Biogas: This is a type of biofuel that is produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as animal waste, food waste, and sewage. Biogas can be used for heating, electricity generation, and transportation.
- Biochar: This is a type of charcoal that is produced by heating organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Biochar can be used as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility and carbon sequestration.
India is a rapidly developing country, with a high demand for energy to support its growth. The country is heavily dependent on fossil fuels, but with the growing concern over environmental issues and climate change, there has been a push to increase the use of renewable energy sources. Biomass is one such source that has been gaining popularity in recent years.
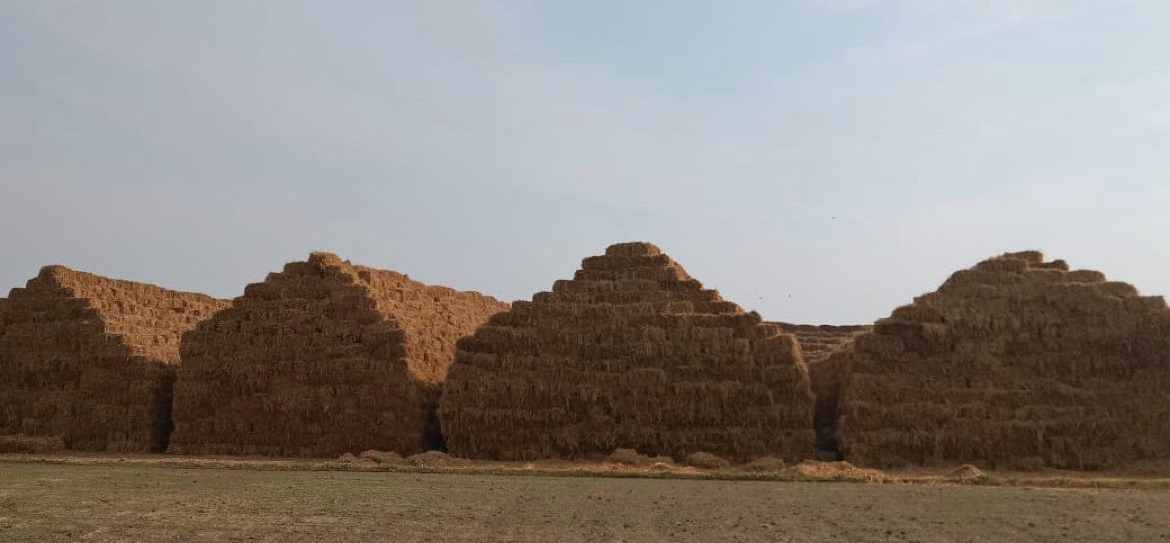

Biomass is an organic matter, such as agricultural waste, forest residue, and municipal solid waste, that can be converted into energy. India has a vast availability of biomass resources, making it an attractive option for energy production. According to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, India’s total biomass potential is estimated to be about 18,000 MW, with the potential to generate 146,500 million units of electricity per year.
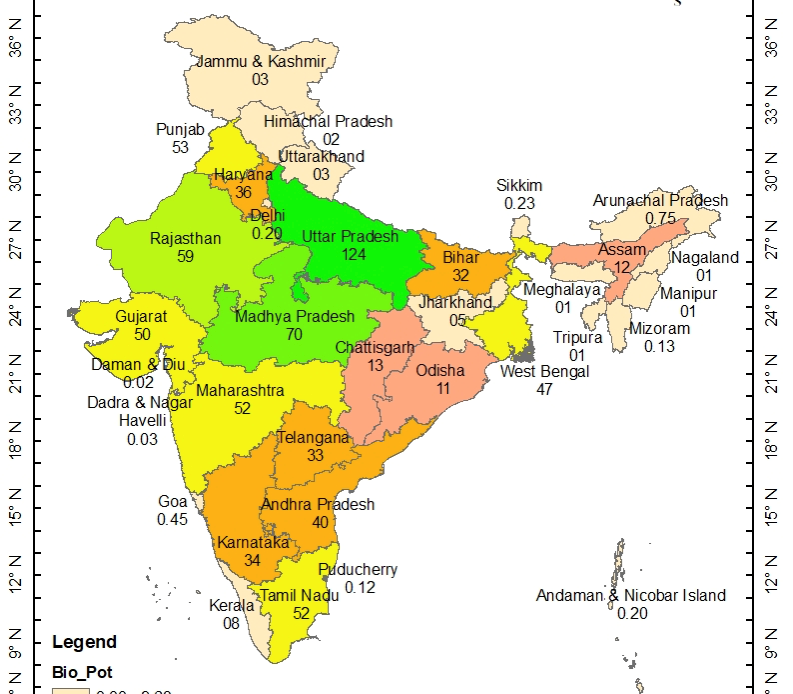
Agricultural waste, such as rice husk, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse, is the largest source of biomass in India. It is estimated that about 754 million tons of agricultural biomass is generated in the country annually out of which 228 million tons of surplus biomass is wasted, which has the energy potential of 28445 MWe and can be used for energy production. Similarly, forest residues, such as tree branches and leaves, can also be used as biomass.
Biomass is used in India in various forms, such as fuelwood, charcoal, briquettes, and pellets. However, the most common use of biomass is for cooking in rural areas, where people rely on traditional stoves and open fires. According to the International Energy Agency, over 800 million people in India still use traditional biomass for cooking, which has severe health implications due to indoor air pollution.
Types of Biomasses in India;
India has a diverse range of biomass resources that can be used for various purposes. Some of the major types of biomasses found in India are:
- Agricultural residues: These include crop residues such as rice straw, wheat straw, sugarcane bagasse, and corn stover. These residues can be used for electricity generation, cooking, and heating.
- Forest biomass: India has a significant amount of forest cover, and the biomass produced from these forests can be used for energy production. This includes wood chips, bark, sawdust, and leaves.
- Animal waste: India has a large livestock population, and the waste generated by these animals can be used for biogas production. Cow dung is the most commonly used animal waste for biogas production in India.
- Municipal solid waste: India generates a significant amount of municipal solid waste, which can be used for biogas production and composting.
- Industrial waste: India has several industries that generate waste products that can be used for energy production. These include rice husk, sugarcane bagasse, and sawdust.
- Aquatic biomass: India has a long coastline and many water bodies, which offer a variety of aquatic biomass resources such as seaweed and aquatic plants.
Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes, such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. Biomass combustion is the most common method used in India, where the biomass is burnt to produce steam, which is then used to generate electricity. Gasification and anaerobic digestion are also being used but on a smaller scale.
Biomass is a promising source of energy in India, as it can help reduce the country’s dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental impact of energy production. Biomass energy also has the potential to generate income for rural communities, as it can provide a source of income for farmers who can sell their agricultural waste to biomass power plants.
Despite the potential of biomass energy, some challenges need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the high cost of setting up biomass power plants, which makes it less attractive to investors. There is also a need for better technology and infrastructure to make biomass energy production more efficient and cost-effective.
The government of India has taken various initiatives in the clean energy transition. Along the same line, two of the missions have been established under two different ministries SAMARTH & SATAT under the Ministry of Power and the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas respectively.
SAMARTH Mission:

- Launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- Aimed at promoting the use of biomass in thermal power plants.
- To have a larger share of carbon-neutral power generation from the thermal power plants.
- The goal is to create an ecosystem for biomass supply chain management, which includes biomass collection, transportation, storage, and processing.
- Focuses on reducing the dependence of thermal power plants on fossil fuels and promoting the use of renewable energy sources like biomass.
- Supports the development of advanced technologies for biomass-based power generation and promotes research and development in the field of biomass utilisation.
SATAT Mission:
- Launched in 2018 by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, Government of India. It was promoted by Indian Oil Marketing Companies like IOCL, HPCL, BPCL, GAIL & IGL.
- The initiative aims to produce compressed biogas (CBG) from waste and bio-mass sources like agricultural residue, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, municipal solid waste (MSW) and sewage treatment plant waste and use of compressed biogas (CBG) as an alternative fuel for transportation.
- The goal is to create a CBG ecosystem in India, which involves setting up CBG plants and supply chain infrastructure for the distribution and marketing of the fuel.
- Focuses on reducing India’s dependence on imported fossil fuels and promoting sustainable and affordable transportation.
- Provides financial incentives and support to entrepreneurs and startups for setting up CBG plants and promoting research and development in the field of CBG.
- The scheme envisages to target production of 15 MMT (million tons) of CBG by 2023, from 5000 Plants.
Why are such missions like SAMARTH and SATAT required?
Missions like SAMARTH and SATAT are required to address some of India’s challenges in energy, environment, and sustainable development.
Here are some reasons why these missions are important:
- Energy security: India is heavily dependent on imported fossil fuels to meet its energy needs, which makes it vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. Promoting the use of renewable energy sources like biomass and compressed biogas can help reduce India’s dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhance its energy security.
- Climate change: Fossil fuels are a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which is a leading cause of climate change. By promoting the use of renewable energy sources, India can reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
- Sustainable development: India is a rapidly developing country with a large population, and meeting the energy needs of its growing economy while ensuring sustainable development is a major challenge. These missions promote the use of renewable energy sources in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner, which is critical for long-term sustainable development.
- Job creation: These missions also have the potential to create employment opportunities in the renewable energy sector and related industries. The SAMARTH mission, for example, aims to create an ecosystem for biomass supply chain management, which has the potential to generate employment opportunities in rural areas.
Biomass supply chain ecosystem
Existing supply chain: India has a significant biomass supply chain, as the country has abundant biomass resources that can be used for energy production. The existing biomass supply chain in India can be described as follows:
- Biomass production: India produces a significant amount of agricultural residues, such as rice straw, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse, which are used as feedstock for bioenergy. Additionally, the country has a large forest cover, which provides a source of forest biomass. Animal waste, municipal solid waste, and industrial waste are also used as biomass feedstock.
- Biomass collection: The collection of biomass in India is often done manually or with the help of small machinery, and the biomass is transported to the processing facility in small quantities.
- Biomass processing: Biomass processing facilities in India are often small-scale and decentralized. Processing methods can include drying, grinding, and pelletizing, and the processed biomass is often used for cooking or heating purposes.
- Biomass transportation: Biomass transportation in India is primarily done by trucks and tractors, as well as by bullock carts in rural areas.
- Biomass utilization: The utilization of biomass in India is primarily for cooking and heating purposes, as well as for electricity generation through small-scale biogas and biomass power plants. Biomass is also used for industrial applications, such as in the paper and pulp industry.
Efficient Biomass Supply Chain: The optimum way of the biomass supply chain depends on various factors such as the type of feedstock, processing technology, and end-use. However, some general principles can be followed to ensure the efficiency and sustainability of the biomass supply chain. Here are some key considerations for optimizing the biomass supply chain:
- Feedstock selection: The selection of feedstock is critical to the efficiency and sustainability of the biomass supply chain. Feedstock should be chosen based on availability, quality, and environmental impact. Ideally, feedstock should be produced sustainably without competing with food production or causing land-use change.
- Logistics optimization: Transportation is a significant cost in the biomass supply chain. The logistics of biomass transport can be optimized by using the most efficient modes of transportation, such as rail or waterways, and by locating processing facilities close to feedstock sources.
- Processing technology: The processing technology used in the biomass supply chain should be selected based on the type of feedstock and the end-user. The most efficient and sustainable processing technology should be selected to maximize the energy output and minimize environmental impact.
- Sustainability assessment: The biomass supply chain should be assessed for sustainability, considering the social, environmental, and economic impacts of each stage. A sustainability assessment should be conducted to identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Collaboration and integration: Collaboration and integration between different stages of the biomass supply chain can improve efficiency and reduce costs. For example, co-locating processing facilities with end-users can reduce transportation costs.
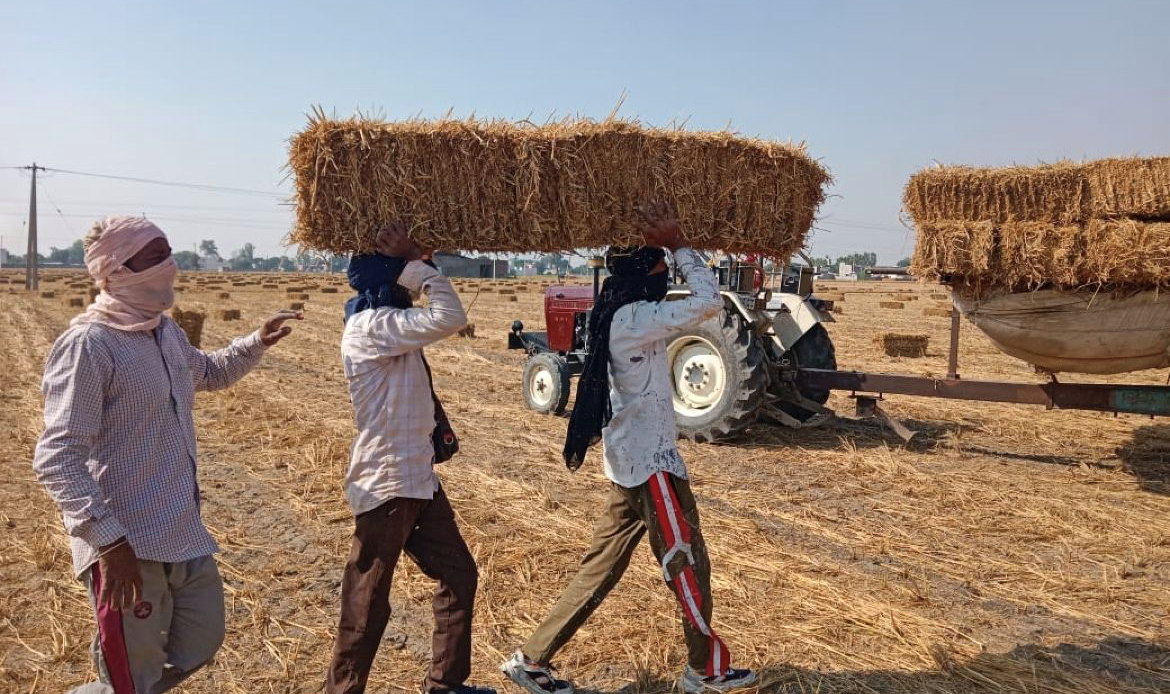

The biomass supply chain in India is facing various challenges, including a need for more infrastructure for large-scale biomass collection and transportation, inadequate processing facilities, and low awareness and adoption of biomass-based technologies. However, the Indian government has implemented various policies and initiatives to promote the use of biomass for energy production.
Overall, optimizing the biomass supply chain requires a holistic approach that considers all stages of the supply chain and the social, environmental, and economic impacts of each stage. By following the above principles, the biomass supply chain can be made more efficient and sustainable.
In summary, missions like SAMARTH and SATAT are important for promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly energy sources, enhancing energy security, reducing carbon emissions, promoting sustainable development, and creating employment opportunities.
In recent years, there has been a push towards using biomass for power generation in India. The government has set targets to increase the share of renewable energy in the country’s energy mix, with a particular emphasis on biomass power generation. The government has launched various schemes and subsidies to promote the use of biomass for electricity generation, such as the biomass power and cogeneration program.
Bioenergy has the potential to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change, as it is a renewable and low-carbon source of energy.
Biomass is a valuable and sustainable source of energy in India, with vast availability and diverse biomass resource base, which can be harnessed to generate electricity and promote rural development. Using biomass energy can help reduce the country’s dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to its economic development. However, there is a need for greater investment in the technology and infrastructure to make biomass energy more cost-effective and efficient.
Biomass energy has significant potential as a renewable and sustainable energy source and can play an important role in transitioning to a more sustainable energy future. Biomass energy can help reduce waste by converting agricultural, forest, and other organic waste materials into useful energy. This can also help reduce pollution and improve air quality, as biomass energy plants can use technology to capture and filter out emissions and other pollutants.
Author
Dharmesh Kumar Kewat
MTech(Thermal), Executive MBA (Energy), Executive, NTPC