The main themes that will likely reshape and transform the sustainability scene in 2024 will have an impact on business practises, laws, technological advancements, and people’s actions, all of which will contribute to a more sustainable future.
Major themes reshaping the sustainability landscape in 2024 are as follows;
- Circular economy adoption
- Climate-tech innovation
- Regenerative practices
- Corporate accountability
- Digitalization for sustainability
- Just transition & social equity
- Global collaboration & policy shifts
- Consumer behaviour shifts
- Resilience & adaptation strategies
- Education and awareness campaigns
The first three circular economy, climate-tech innovation, and regenerative agriculture will be discussed in detail in the current article.
Embracing circular economy: Redefining business practices for a sustainable future
In a world brimming with resource challenges and environmental concerns, the concept of a circular economy stands tall as a beacon of hope, offering a transformative approach towards sustainability. The shift towards a circular economy marks a paradigmatic shift from the traditional ‘take-make-dispose’ model to a more regenerative system, where resources are utilised efficiently, reused, repurposed, and recycled to minimize waste and maximise value.
Understanding the circular economy
At its core, a circular economy is a restorative and regenerative system that aims to keep products, components, and materials at their highest utility and value at all times. Unlike the linear economy, where resources are extracted, processed into goods, and eventually discarded as waste, the circular economy model envisions a closed-loop system, where materials and products continually circulate within the economy.
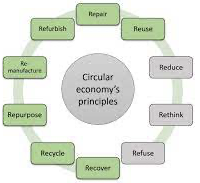
Principles of circular economy adoption;
Designing for durability and reusability: Central to the circular economy ethos is the concept of designing products for longevity, repairability, and reusability. Companies are increasingly focusing on creating products that can be easily disassembled, repaired, or upgraded, prolonging their lifecycle and reducing the need for constant replacements.
Promoting recycling and material recovery:
Embracing recycling and material recovery processes is pivotal. Companies are exploring innovative recycling technologies to repurpose materials and reduce reliance on virgin resources. This includes initiatives to use recycled materials in manufacturing and to invest in infrastructure that supports efficient recycling.
Shifting to service-oriented models:
Moving away from the traditional ownership model, businesses are embracing service-oriented models. Services such as product leasing, sharing, and subscription-based models not only reduce resource consumption but also foster a culture of access over ownership.

Collaboration and value chain optimization:
Circular economy principles emphasize collaboration across industries and value chains. Companies are forging partnerships to optimize resource use, share knowledge, and develop innovative solutions for recycling, reusing, and repurposing materials.
Benefits and impact
The adoption of circular economy principles brings forth a multitude of benefits. Not only does it reduce the strain on finite resources, but it also mitigates environmental degradation, decreases waste generation, and minimizes greenhouse gas emissions. Economically, it fosters innovation, stimulates job creation in new sectors, and enhances overall resource productivity.
Challenges and Road Ahead
While the concept of a circular economy holds immense promise, its widespread adoption faces challenges. These include the need for policy support, investment in infrastructure, technological advancements, behavioural shifts in consumer habits, and a shift in traditional business mindsets.
The transition towards a circular economy is not merely an option but a necessity in the pursuit of a sustainable future. Companies that embrace circularity not only contribute to environmental preservation but also gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market driven by conscious consumerism and regulatory shifts.
In essence, the circular economy represents a holistic approach, aligning economic growth with environmental responsibility. Its adoption is not just a business strategy but a collective commitment towards ensuring a thriving planet for generations to come.

Climate-tech innovation: Pioneering solutions for a sustainable future
The urgency of addressing climate change has spurred a wave of unprecedented innovation in climate-related technologies. This surge in climate-tech innovation holds immense promise, offering scalable solutions to combat the pressing challenges of our changing climate. From renewable energy to carbon capture, sustainable agriculture, and eco-friendly transportation, advancements in these areas are paving the way towards a more sustainable future.

Renewable energy revolution:
At the forefront of climate-tech innovation lies the renewable energy revolution. Breakthroughs in solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy technologies are reshaping the global energy landscape. Solar power innovations, such as improved photovoltaic cells and concentrated solar power systems, are making solar energy more efficient and cost-effective. Similarly, advancements in wind turbine designs and grid integration are driving the growth of wind power as a major renewable energy source.

Carbon capture and sequestration:
Another critical area of focus is carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) technologies. Innovations in CCS aim to capture carbon dioxide emissions from power plants, industrial facilities, and even directly from the atmosphere. Advancements in carbon capture methods, such as direct air capture and utilization, are being explored to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and either store it underground or utilize it in manufacturing processes.

Sustainable agriculture and food systems:
Climate-tech innovations are also revolutionizing agriculture and food systems. Sustainable agricultural practices leveraging technology, such as precision farming, smart irrigation systems, and vertical farming, aim to reduce carbon emissions, conserve water, and optimize land use. Additionally, advancements in crop genetics and bioengineering are fostering the development of climate-resilient crops capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions.

Eco-friendly transportation solutions:
In the transportation sector, the focus is on developing eco-friendly alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Electric vehicles (EVs) are experiencing significant advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and range, making them more accessible and appealing to a broader market. Additionally, innovations in hydrogen fuel cells, biofuels, and sustainable aviation fuels offer promising alternatives to conventional fossil fuels in various modes of transportation.
Impact and challenges ahead:
The impact of climate-tech innovation extends far beyond reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It drives economic growth, creates jobs in emerging industries, and enhances energy security while mitigating the adverse effects of climate change. However, challenges such as scalability, investment needs, policy support, and public adoption remain crucial hurdles to overcome.
The surge of climate-tech innovation represents a beacon of hope in the fight against climate change. Embracing these advancements not only accelerates the transition to a low-carbon economy but also underscores the potential for technological ingenuity to shape a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
Regenerative agriculture: Cultivating a sustainable future
In the realm of agriculture, a profound shift towards regenerative practices is gaining momentum. Regenerative agriculture goes beyond sustainability; it embodies a holistic approach that aims not only to sustain but to regenerate ecosystems, enhance soil health, and restore biodiversity. This transformative approach is poised to revolutionize agricultural systems by nurturing soil vitality, sequestering carbon, and fostering resilience in the face of environmental challenges.

Understanding regenerative agriculture:
At its core, regenerative agriculture is a set of farming and land-use practices designed to mimic and enhance natural processes. It revolves around nurturing the health of the soil ecosystem, focusing on principles such as minimal soil disturbance, crop rotation, cover cropping, and diverse plantings. These practices encourage soil regeneration, promote biodiversity, and contribute to carbon sequestration.

Restoring soil health and biodiversity:
Central to regenerative agriculture is the recognition that healthy soils are the foundation of a thriving ecosystem. Practices like no-till or reduced tillage minimize soil disturbance, preserving its structure and fostering microbial activity crucial for nutrient cycling. Cover crops and diverse plantings not only protect the soil from erosion but also enrich it by fixing nitrogen, increasing organic matter, and fostering beneficial soil organisms.

Carbon sequestration and climate resilience:
Regenerative practices play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. Healthy soils enriched with organic matter act as carbon sinks, drawing down atmospheric CO2 and storing it in the soil. This not only contributes to climate change mitigation but also enhances the soil’s water retention capacity, crucial for building resilience against extreme weather events.
Benefits beyond agriculture:
The impact of regenerative agriculture transcends the boundaries of farms. Restoring biodiversity and enhancing soil health supports wildlife habitats, promotes water quality, and contributes to overall ecosystem health. Moreover, healthier soils lead to increased agricultural productivity, reducing the need for synthetic inputs and fostering economic viability for farmers.
Challenges and opportunities:
While the benefits of regenerative agriculture are promising, challenges such as transitioning from conventional practices, knowledge dissemination, and initial investment costs hinder widespread adoption. However, initiatives promoting education, research, policy support, and farmer networks are paving the way for a smoother transition and wider adoption of regenerative practices.
Regenerative agriculture stands as a beacon of hope in addressing the interconnected challenges of food security, climate change, and environmental degradation. Embracing these practices not only revitalizes agricultural landscapes but also holds the potential to transform our relationship with the land, fostering a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
In 2024, the trajectory of sustainability hinges on the convergence of three pivotal concepts: Circular economy adoption, climate-tech innovation, and regenerative practices. The world is witnessing a transformative shift towards the circular economy, a model where resources are conserved, reused, and recycled, ultimately reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Concurrently, the rise of climate-tech innovation showcases the development of revolutionary technologies focused on mitigating climate change and fostering sustainable practices across industries. These innovations pave the way for a greener future, incorporating renewable energy, carbon capture, and eco-friendly solutions. Complementing these advancements, Regenerative practices underline a holistic approach, emphasizing restoration and enhancement of ecosystems, aiming not just for sustainability but for actively improving environmental conditions. Together, these three pillars represent a bold direction towards a more harmonious relationship between humanity and the planet.
“In embracing circular economy adoption, climate-tech innovation, and regenerative practices, we embark on a collective journey towards a sustainable and thriving future. As we navigate the challenges of our time, these pillars serve as beacons of hope, guiding us towards a world where ecological balance and human prosperity coexist. Now more than ever, our actions shape the trajectory of tomorrow. Let us heed the call to embrace these transformative ideas, uniting our efforts to safeguard our planet and ensure a legacy of sustainability for generations to come.”
Author
Dr. Yogita Deshmukh
PhD. Life Sciences
Co-Founder GANAR BIOFUELS
BIOCHAR EXPERT
CERTIFIED INDEPENDENT DIRECTOR